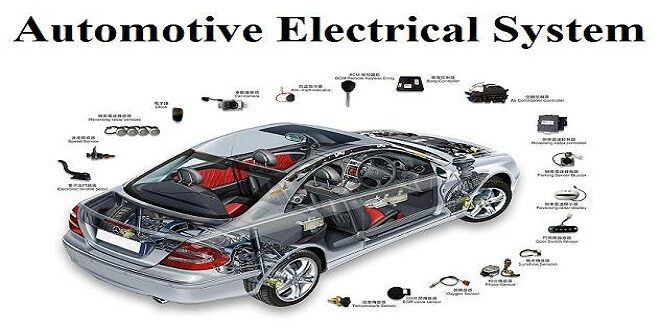
The automobile uses a variety of electrical accessories for different purposes. This section describes the construction and working of battery which is the source of electricity in automobiles. The module enables the students to trace different electrical circuits like lighting circuits, direction indicator circuits, brake light circuits, horn circuits, etc. For starting a vehicle we have to crank the engine by using starting motor, for igniting the fuel in the engine an electric spark is used, for charging the battery in the vehicle the charging system is a must.
The module deals with all these areas in detail. The module also explains the emission control system used in automobiles which is most relevant nowadays. The concepts of euro norms implementation in India and different emission control systems used for minimizing pollution are explained thoroughly. Safety features commonly used in automobiles like airbags, seat belts, etc. are also mentioned in this module. The module on automotive electrical systems provides a wide range of job opportunities in the automobile industry
Automotive battery
The battery is the heart of any automotive electrical system. It is the source of electricity. It is a rechargeable battery that supplies electric energy to an automobile. This unit elaborates on the types, construction, and working of batteries. Care and maintenance, characteristics of batteries, charging methods, and battery testing are other key topics in this unit.
Battery
A battery is an electrochemical device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy when discharging and electrical energy to chemical energy while charging. The main purposes of the battery are to store electrical energy and to provide a supply of current for cranking the starting motor and for other electrical units.
Container
They are of single-piece construction made of polypropylene which is very strong and lightweight plastic. There are partitions inside the container for different cells. To avoid the short of positive and negative plates, bridges are formed at the bottom of the container.
Plates
There are two types of battery plates
- Positive plate
- Negative plate
For each plate, there is a supporting grid made of an alloy of lead and antimony. The function of the grid is to hold the active material and to carry current in the plates. The active material in the positive plate grid is lead peroxide (PbO2) in chocolate color and the negative plate is spongy lead(Pb) in grey color. These plates are immersed in dilute sulphuric acid.
There are separators to keep the positive and negative plates apart. These separators are made of non – conducting porous materials and prevent short circuits. A number of positive plates are lead burnt to a post strap to form a positive plate group; while the negative plate group contains one plate more than positive group so that both sides of positive plates can be utilized as the greater electrochemical activity takes place. The positive plate post is usually larger in diameter than the negative plate.
Cells
One positive and one negative group of plates are slid over each other with separators in between, to form a cell. Each cell supplies a current of 2V, a12 volt battery consists of 6 cells. The size of the plates and their number per cell determines the capacity of the battery. Cells are connected in series.
Last word
After assembling completely, the battery is filled with electrolytes. It is a solution of water and sulphuric acid. It contains approximately one part of sulphuric acid and two parts of water by volume.
 Tech Readers
Tech Readers