‘Earth is a livable planet’. This is the most heard information about the planet Earth. Have you ever thought about what makes the Earth a livable place? To live, the most important component is the air to breathe. The blanket of air that encircles the Earth is responsible for the climatic conditions and seasonal changes. This blanket of air is known as the atmosphere. It is also responsible for the coldness or hotness which we feel. Morning chillness and afternoon sweating are also because of the atmosphere that surrounds the Earth.
There are many devices to measure the temperature, pressure, and humidity present in the air. Let us learn the layers of the atmosphere, what is humidity, and also about the humidity measuring device.
What is Humidity
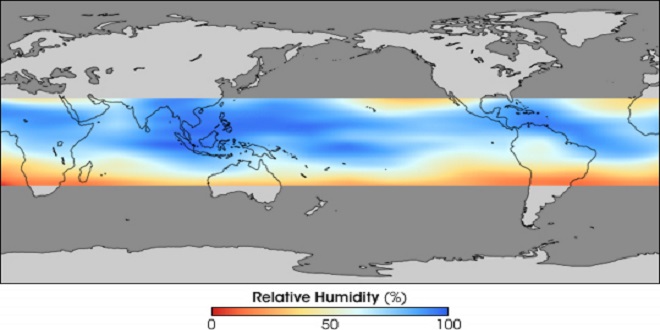
Earth’s atmosphere consists of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), other gasses (0.1%) as well as water vapour. Other gasses include carbon dioxide, methane, water vapour, and neon. The amount of water vapour in the air gives the humidity in the atmosphere.
Humidity is high in the warm air due to the presence of high water content at higher temperatures. Low humidity is seen in the cold air since it cannot retain moisture. Hence the air is dry. This is the main reason why we experience much dryness in the winter. Even in freezing temperatures, small amounts of water vapour exists. Humidity is of three types, they are:
- Absolute Humidity
- Relative Humidity
- Specific Humidity
The humidity is expressed as grams of moisture per cubic meter of the air, and there is no SI unit for measuring humidity. Humidity is measured using a special apparatus called a hygrometer. A hygrometer is used in calculating the moisture content in the air or enclosed areas. It finds its application in museums, agricultural fields, manufacturing industries, hospitals, food preservation, and meteorology. There are many types of hygrometers classified based on their design and use.
What are the Layers Present in Atmosphere
Before knowing about the layers of the atmosphere, let us know what is meant by the atmosphere. It is a blanket of gasses that encircle the Earth. The atmosphere is held by the gravitational force of attraction. Atmosphere aids in retaining the heat from the main source of light – the Sun. It also helps to stop the Sun’s radiation from breaking out into space. It is one of the key elements in maintaining the water cycle on the Earth. It is the main source of living since it contains oxygen and carbon dioxide.
The five layers of the atmosphere are:
- Exosphere
- Thermosphere
- Mesosphere
- Stratosphere
- Troposphere
The troposphere extends about 10 km above sea level from ground level and is the lowest layer in the atmosphere. It contains the highest amount of total water vapour, and hence clouds appear in this layer. The stratosphere lies above the troposphere and extends from about 50 km above the ground. The mesosphere extends about 85 km from the ground. The mesosphere can reach –90°C and is the coldest region. Above the mesosphere lies the thermosphere. The thermosphere is a region in which the temperature keeps increasing as you move up.
 Tech Readers
Tech Readers